A simple pinhole camera model. More...
#include <PinholeCameraModel.hpp>
Public Types | |
| enum | Error { NOT_ENOUGH_INPUT_DATA, UNEQUAL_CARDINALITY_OF_INPUT_SETS, UNKNOWN_ESTIMATION_METHOD, UNKNOWN_ERROR } |
| enum | Constraints { NO_SKEW, SAME_FOCAL_LENGTHS, SAME_FOCAL_LENGTHS_AND_NO_SKEW } |
Public Member Functions | |
| PinholeCameraModel () | |
| Constructor. | |
| virtual | ~PinholeCameraModel () |
| Destructor. | |
| Vector3T | getCameraPosition () const |
| Returns the camera's position in world coordinates. | |
| Matrix3T | getCameraOrientation () const |
| Returns the camera's orientation in world coordinates. | |
| Matrix4T | getExtrinsicParameters () const |
| Returns the extrinsic camera parameters (position and orientation) as homogeneous matrix. | |
| Matrix34T | getIntrinsicParameters () const |
| Returns the intrinsic camera parameters. | |
| Matrix34T | getCameraParameters () const |
| Returns the projection matrix. | |
| std::tuple< T, T > | getFocalLengths () const |
| Returns the focal lengths in x- and y-direction. | |
| std::tuple< T, T > | getImageCenter () const |
| Returns the image center a.k.a. principal point. | |
| T | getSkew () const |
| Returns the skew in the image plane. | |
| void | setCameraPosition (const Vector3T &position) |
| Set the camera's position in world coordinates. | |
| void | setCameraOrientation (const Matrix3T &orientation) |
| Set the camera's orientation in world coordinates. | |
| void | setExtrinsicParameters (const Matrix4T ¶meters) |
| Return the extrinsic camera parameters (position and orientation) as homogeneous matrix. | |
| void | setIntrinsicParameters (const Matrix34T ¶meters) |
| Return the intrinsic camera parameters. | |
| void | setFocalLengths (T f_x, T f_y) |
| Set the focal lengths in x- and y-direction. | |
| void | setImageCenter (T c_x, T c_y) |
| Set the image center a.k.a. principal point. | |
| void | setSkew (T skew) |
| Return the skew in the image plane. | |
| Vector2T | operator* (const Vector3T &point) const |
| Transforms / projects a 3D point onto the image plane. | |
| Vector2T | transform (const Vector3T &point) const |
| Transforms / projects a 3D point onto the image plane. | |
| T | estimate (const Range< Vector3T > &points_world, const Range< Vector2T > &points_display) |
| Estimates the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from two corresponding point sets. | |
| T | estimateWithConstraints (const Range< Vector3T > &points_world, const Range< Vector2T > &points_display, Constraints constraints=SAME_FOCAL_LENGTHS_AND_NO_SKEW, bool initialize=true, bool constrained_decomposition=true) |
| Estimates the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from two corresponding point sets. | |
A simple pinhole camera model.
| T | scalar (floating point) type |
This class implements a simple pinhole camera model. The model parameters can be set / modified by the user or estimated given a set of corresponding point pairs.
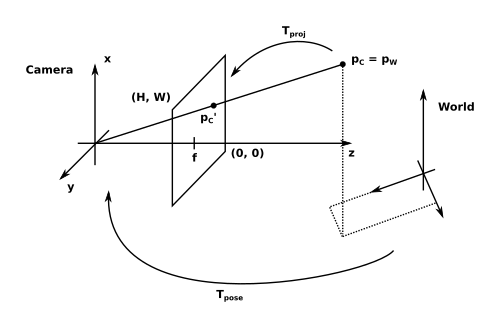
Pinhole camera model.
The camera is modeled by a projection matrix \( T_{proj} \) which maps a three-dimensional point \( p \) to the two-dimensional point \( p' = T_{proj} * p \) that lies in the image plane of the camera. The optical properties of the camera are defined by the focal lengths \( f_x \) and \( f_y \), the image center \( (c_x, c_y) \) where the optical axis intersects the image plane, and a parameter \( \tau \) which models the skew of the image plane axes. The camera's pose (i.e., its location and orientation) in world coordinates is described by the mapping \( T_{pose} \) which maps from the world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system. Thus, the overall system is described with the following equation:
\[ p' \sim T_{proj} T_{pose} p \]
Here, the matrix entries are described in more detail:
\[ \begin{pmatrix} x' \\ y' \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \sim \begin{pmatrix} f_x & \tau & c_x & 0 \\ 0 & f_y & c_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_1 \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_2 \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} & t_3 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \]
For more details, please be referred to [1], [2], [3], and [4].
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <vector> #include<Eigen/Core> #include<Eigen/StdVector> #include <TRTK/Coordinate.hpp> #include <TRTK/PinholeCameraModel.hpp> #include <TRTK/Tools.hpp> #include <TRTK/Transform3D.hpp> using namespace Eigen; using namespace std; using namespace TRTK; using namespace TRTK::Tools; using Point3D = PinholeCameraModel<double>::Vector3T; using Point2D = PinholeCameraModel<double>::Vector2T; struct GenerateTestData { GenerateTestData() { // Instantiate a pinhole camera model. PinholeCameraModel<double> camera_model; // Set the intrinsic camera parameters. camera_model.setFocalLengths(80, 79); camera_model.setImageCenter(250, 251); camera_model.setSkew(0.1); // Set the extrinsic camera parameters. Transform3D<double> T; T.rotateAxis(40, Point3D(1, 2, 3), Transform3D<double>::DEGREES); T.translate(130, 135, 90); camera_model.setExtrinsicParameters(T.getTransformationMatrix()); // Generate some test data. const int number_of_points = 6; for (int i = 0; i < number_of_points; ++i) // generate points in the world COS { auto x = randn(0.0, 30.0); // in the camera COS auto y = randn(0.0, 30.0); // in the camera COS auto z = randn(600.0, 10.0); // in the camera COS Point3D p = T.inverse() * Point3D(x, y, z); // in the world COS points_world.emplace_back(p); } for (auto const & p_W : points_world) // generate points in the camera COS { Point2D p_D = camera_model.transform(p_W); points_display.push_back(p_D); } } vector<Point3D> points_world; vector<Point2D> points_display; // image plane }; int main() { srand(0); GenerateTestData test_data; PinholeCameraModel<double> model; auto rmse = model.estimate(make_range(test_data.points_world), make_range(test_data.points_display)); cout << setprecision(4); cout << fixed; cout << "RMSE: " << rmse << endl << endl; cout << "Extrinsic camera parameters: " << endl << model.getExtrinsicParameters() << endl << endl; cout << "Intrinsic camera parameters: " << endl << model.getIntrinsicParameters() << endl; return 0; }
RMSE: 0.0000
Extrinsic camera parameters:
0.7828 -0.4820 0.3937 130.0000
0.5488 0.8329 -0.0715 135.0000
-0.2935 0.2721 0.9164 90.0000
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 1.0000
Intrinsic camera parameters:
80.0000 0.1000 250.0000 0.0000
0.0000 79.0000 251.0000 0.0000
0.0000 0.0000 1.0000 0.0000
The estimateWithConstraints() function is only available if the CPPOPTLIB_FOUND macro is defined. Then, the include directory of the CppOptimizationLibrary must be set appropriately. In CMake you might want to insert the following lines in your CMakeLists.txt file.
find_path(CPPOPTLIB NAMES cppoptlib cppoptlib-1.0.0)
if(CPPOPTLIB)
set(CPPOPTLIB_FOUND 1)
include_directories(${CPPOPTLIB})
add_definitions(-DCPPOPTLIB_FOUND)
endif()
The library can be found at https://github.com/PatWie/CppNumericalSolvers .
[1] Hartley and Zisserman, "Multiple view geometry in computer vision", 2003
[2] Szeliski, "Computer Vision - Algorithms and Applications", 2011, Springer
[4] Sutherland, "Three-Dimensional Data Input by Tablet", 1974, IEEE
[3] Tuceryan et al., "Single point active alignment method (SPAAM) for optical see-through HMD calibration for AR", 2000, IEEE
Definition at line 348 of file PinholeCameraModel.hpp.
| enum TRTK::PinholeCameraModel::Constraints |
Definition at line 358 of file PinholeCameraModel.hpp.
| T TRTK::PinholeCameraModel< T >::estimate | ( | const Range< Vector3T > & | points_world, |
| const Range< Vector2T > & | points_display | ||
| ) |
Estimates the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from two corresponding point sets.
| [in] | points_world | 3d points in the world coordinate system. |
| [in] | points_display | Corresponding 2d points in the image plane. |
The intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters are estimated from two corresponding point sets (i.e., the i-th elements of both point sets correspond to each other). It is assumed that the camera is fixed in the world coordinate system (COS) and that the transition from the world COS into the camera COS is described by the pose matrix.
The 2d points \( (x'_i, y'_i)^T \) in points_display are assumed to be normalized:
\[ \begin{pmatrix} x'_i \\ y'_i \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} u_i / w_i \\ v_i / w_i \end{pmatrix}, \quad \begin{pmatrix} u_i \\ v_i \\ w_i \end{pmatrix} = T_{proj} T_{pose} \begin{pmatrix} x_i \\ y_i \\ z_i \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \]
At least 6 corresponding point pairs must be given. The focal lengths are assumed to be positive.
If \( f \) describes the above mapping, i.e., \( p' = f(p) \) with \( p' = (x', y')^T \) and \( p = (x, y, z)^T \), then this function returns the root mean square error
\[ rmse = \sqrt{ \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^N \left\Vert \hat f(p_i) - p'_i \right\Vert^2 } \]
where \( \hat f \) is the function estimate.
| ErrorObj | If the input set sizes do not match, an error object is thrown and its error code is set to UNEQUAL_CARDINALITY_OF_INPUT_SETS. |
| ErrorObj | If there are not enough point pairs (at least six), an error object is thrown and its error code is set to NOT_ENOUGH_POINTS. |
Definition at line 496 of file PinholeCameraModel.hpp.
| T TRTK::PinholeCameraModel< T >::estimateWithConstraints | ( | const Range< Vector3T > & | points_world, |
| const Range< Vector2T > & | points_display, | ||
| Constraints | constraints = SAME_FOCAL_LENGTHS_AND_NO_SKEW, |
||
| bool | initialize = true, |
||
| bool | constrained_decomposition = true |
||
| ) |
Estimates the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from two corresponding point sets.
| [in] | points_world | 3d points in the world coordinate system. |
| [in] | points_display | Corresponding 2d points in the image plane. |
| [in] | constraints | Constraints with respect to the projection matrix. |
| [in] | initialize | See below for more details. |
| [in] | constrained_decomposition | See below for more details. |
This function estimates the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from two corresponding point sets (i.e., the i-th elements of both point sets correspond to each other). The estimation is constrained in such a way that the focal lengths \( f_x \) and \( f_y \) are equal and/or the skew parameter \( \tau \) is zero.
It is assumed that the camera is fixed in the world coordinate system (COS) and that the transition from the world COS into the camera COS is described by the pose matrix. The 2d points \( (x'_i, y'_i)^T \) in points_display are assumed to be normalized:
\[ \begin{pmatrix} x'_i \\ y'_i \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} u_i / w_i \\ v_i / w_i \end{pmatrix}, \quad \begin{pmatrix} u_i \\ v_i \\ w_i \end{pmatrix} = T_{proj} T_{pose} \begin{pmatrix} x_i \\ y_i \\ z_i \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \]
At least 6 corresponding point pairs must be given. The focal lengths are assumed to be positive.
If initialize is set to true, the camera parameters are estimated by calling estimate(). Thereby, the internal parameters are overwritten. If the flag is set to false, the currently set camera parameters are used during the optimization.
The camera parameters are decomposed into the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters using the RQ decomposition. Then, these two matrices are modified during the iterative optimization procedure in order to reduce the root mean square error. The user-specified constraints are taken into account during the optimization but not when decomposing the camera parameters. By setting the constrained_decomposition flag to true, the constraints are also taken into account when performing the decomposition. Depending on the nature of the data the one or other may be more advantageous.
If \( f \) describes the above mapping, i.e., \( p' = f(p) \) with \( p' = (x', y')^T \) and \( p = (x, y, z)^T \), then this function returns the root mean square error
\[ rmse = \sqrt{ \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^N \left\Vert \hat f(p_i) - p'_i \right\Vert^2 } \]
where \( \hat f \) is the function estimate.
| ErrorObj | If the input set sizes do not match, an error object is thrown and its error code is set to UNEQUAL_CARDINALITY_OF_INPUT_SETS. |
| ErrorObj | If there are not enough point pairs (at least six), an error object is thrown and its error code is set to NOT_ENOUGH_POINTS. |
This function is only available if the CPPOPTLIB_FOUND macro is defined. Then, the include directory of the CppOptimizationLibrary must be set appropriately. In CMake you might want to insert the following lines in your CMakeLists.txt file.
find_path(CPPOPTLIB NAMES cppoptlib cppoptlib-1.0.0)
if(CPPOPTLIB)
set(CPPOPTLIB_FOUND 1)
include_directories(${CPPOPTLIB})
add_definitions(-DCPPOPTLIB_FOUND)
endif()
The library can be found at https://github.com/PatWie/CppNumericalSolvers .
Definition at line 1117 of file PinholeCameraModel.hpp.
Documentation generated by Doxygen